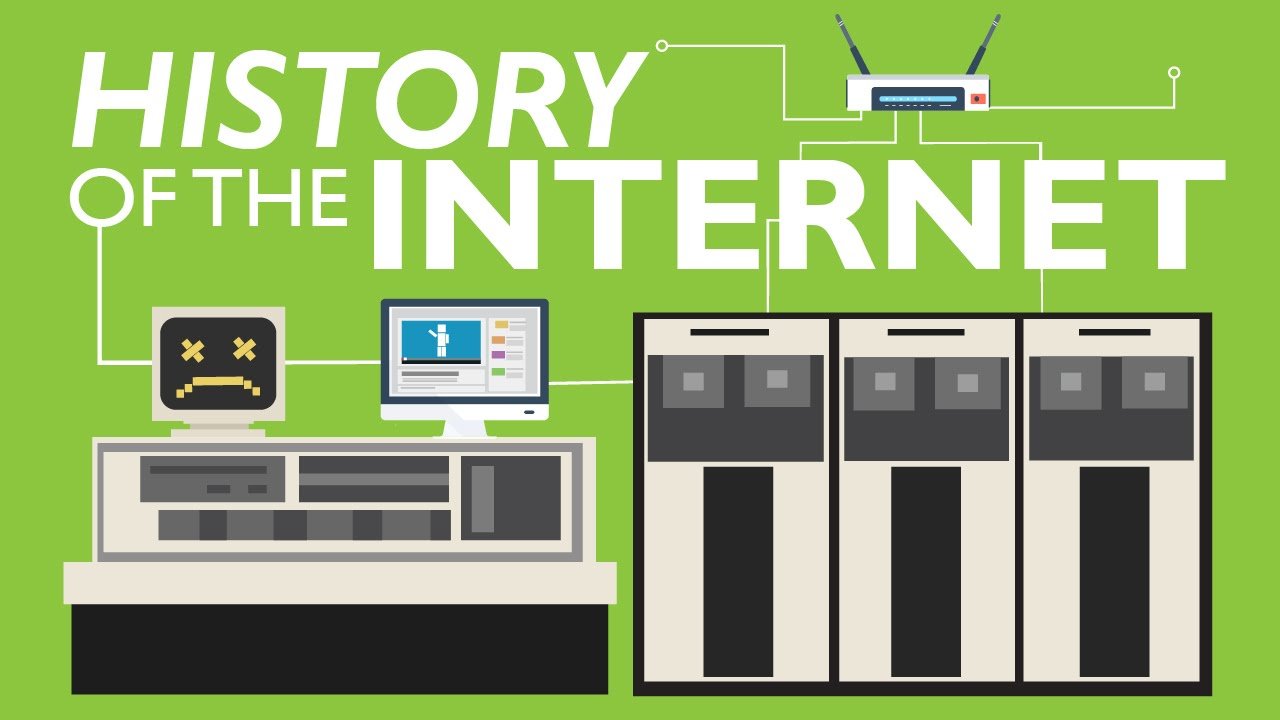
Invention of the Internet from early history to now
It seems like the invention of the Internet has always been there because it plays such a significant role in our daily lives. However, the internet’s history did not start until the 1950s. It took several decades for it to develop into what it is today.
The internet, once only accessible to researchers and scientists, is now available to everyone for use and entertainment. Well, what is the internet? The Internet is a global network of connected computers and other devices for information sharing and communication.

It has many smaller networks than Individuals, companies, governments, and educational organizations. This is the fundamental idea behind how the Internet works. A physical infrastructure consisting of cables, satellite links, and wireless connections links these networks. However, when and how did the internet invention start?
ARPANET- the beginning of the Internet (1969)
ARPANET refers to the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network. It was the first wide-area packet-switched computer network that the US military started using to link computers far apart in the late 1960s. It used packet-switching to send messages across.
The first Email invention (1971)
The first message on ARPANET was sent from one computer to another in 1969. But it was not quite like today’s emails. However, Ray Tomlinson changed that by adding the @ symbol in 1971, making email addresses as we know them.
Initially, universities used emails, but it became popular rapidly for professional communication. ISPS (Internet Service Providers) offered free email and web-based services in the 1990s, like Hotmail and Yahoo, which made emails even more widespread. However, e-mail was a common way to communicate digitally using a phone in the 2000s.
ARPANET switches to TCP/IP (1983-1985)
ARPANET used NCP (Network Control Protocol) for communication before 1983, but it had limitations. So, internet developers made TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), which could connect different networks.
DNS comes into play (1985)
The internet invention became more developed with the emergence of DNS (Domain Name System) in 1985. ISPs created DNS in 1984 to translate human-readable domain names into numerical IP addresses.
IP addresses serve as an internet address book. It made remembering domain names easier as google.com instead of a complicated series of numerical characters. DNS facility was available for common users in 1985.
The launch of AOL (1985)
AOL (America Online) is an American online service provider and web portal based in New York City. It was launched in 1985. It made the Internet accessible to millions of users.
AOL offered easy-to-use dial-up access, connecting home users via phone lines. This opened the internet to everyone, not just businesses and institutions. It established social interaction through chat rooms and communities, developing the Internet into the digital world as it is today.
IRC for direct messaging (1988)
A Finnish computer scientist, Jarkko Oikarinen, created IRC (Internet Relay Chat) in 1988 for group communication, discussion forums, private messaging, data transfer, and file sharing among users in different locations.
The beginning of the World Wide Web (1989)
British scientist Tim Berners-Lee, working at CERN (the European Organization for Nuclear Research) came up with the idea for the World Wide Web (www). He created key technologies like URLs, HTTP, and HTML to link documents on various computers. It made the web accessible from anywhere.
The first commercial dial-up ISP (1989)
The first commercial Internet service provider (ISP) was “The World” developed by Joel Furr in 1989. It provided intent access to people of the San Francisco Bay Area.
This ISP offered user-friendly tools like the Web Explorer browser and services, email, and file sharing. It expanded Internet use beyond institutions to a broader audience and inspired the creation of other ISPs worldwide.
The first search engine (1990)
Alan Emtage created the first search engine Archie, which indexed files on FTP (File Transfer Protocol) sites in 1990. Archie could not search within web pages and indexed only particular file formats compared to modern search engines.
However, it opened the way for the most advanced search engines like Gopher and eventually led to popular ones like Google (1998).
The first webpage (1991)
Tim Berners-Lee developed the first webpage in 1991 with a simple design and plain text. It provided an overview of the www project, hypertext, and how to create web pages. It included hyperlinks to moving to other documents.
The first webcam (1991)
Researchers at the University of Cambridge introduced the first webcam called the “coffee pot cam” in 1991 to monitor the coffee levels in pots. Hence, users could check if the pot was full without leaving their desks by viewing images uploaded to a web page.
The first photo uploaded (1992)
Tim Berners-Lee shared a picture of four women, the members of the parody musical group Les Horribles Cernettes or the Horrible CERN Girls in 1992. Internet invention took a turn with this picture emergence in the basic GIF format.
Government Participation (1993)
US President Bill Clinton introduced the National Information Infrastructure (NII) in 1993. The purpose was to develop policies and the necessary infrastructure to support internet expansion and universal access. NII also addresses issues like privacy, security, and intellectual property rights.
First secure e-commerce transaction (1994)
Phil Brandenberger, bought Sting’s album “Ten Summoner’s Tales” online in 1994, marking the first secure online transaction. He used the Netscape Navigator browser on the NetMarket website, paying $12.45 for the CD album and $4.95 for shipping.
This transaction used SSL, a security protocol by Netscape, using credit card information for a safe transfer. Before this, the Internet Shopping Network (ISN) started selling several products like books and flowers in 1992.
The first social media platform (1996)
Andrew Weinrich launched the first social media platform, “Six Degrees,” in 1996, containing customizable profiles, friend lists, school affiliations, and messaging. This invention initiated a revolutionary process of social media platforms in the internet field.
Wi-Fi Invention (1997)
Wireless fidelity (or simply Wi-Fi) is a technology that allows electronic devices to connect to the internet and communicate over local area networks wirelessly. A team of researchers from NCR Corporation created the first wireless called IEEE 802.11.
Invention of Google (1998)
Two Standford University students, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, developed the Google search engine in 1998. It was one of the most advanced internet inventions throughout history. They had already registered the domain google.com in 1997 for this search engine.
This search engine has been expanding and launching several innovative products and services since that day. It includes Google Ads, Google Maps, Google Drive, etc.
The launch of Wikipedia (2001)
Jimmy Wales and Larry Sanger launched Wikipedia in 2001. It is one of the most widely used online platforms to gain information about anything. You can add, edit, and modify content as it is accessible to everyone via the internet.
MySpace launching (2003)
Tom Anderson and Chris DeWolfe introduced a social networking platform named “MySpace.” It allows you to create customized profiles, socialize with friends, and share photos and music.
Digg website (2004)
Digg was a social news website launched in 2004 to provide newsworthy content to readers. It also allowed users to submit links to news articles, blog posts, images, and videos. It became the most visited website on the internet in 2008.
iPhones and the Mobile Web (2007)
iPhone changed the dynamic of the mobile phone industry and mobile web with its launch in 2007. It introduced a powerful browser, Safari, which allowed users to access and browse the internet on mobile devices. It ended internet limitation to desktops only.
Bitcoin’s arrival in the market (2009)
The Bitcoin introduction in the market also boosted the internet invention to the next level in 2008. It is a cryptocurrency that works to secure transactions without the control of main authorities like governments or financial institutions.
ICANN policy changes (2009)
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) implemented several policy changes for domain name registration and general Internet management in 2009. These changes made the domain name registration process more accessible and protected the interests of internet users than before.

2010-2019
Social media platforms expanded, smart technologies, and e-commerce partially replaced the physical shopping trend. It set digital trends including streaming services, mobile games, viral content, and AI technology evolving for the future.
Social media growth
- Facebook: dominated social media and acquired WhatsApp and Instagram
- Twitter X: engaged millions of users to keep them updated on current world affairs, especially in the political category
- Instagram: dominated social media becoming the leading photo and video-sharing platform for influencers, celebrities, brands, etc
- Snapchat: launched disappearing photo and video messages and stories which other social media platforms later adopted.
- Pinterest: became the leading platform for visual content through sharing images regarding user’s interests
- LinkedIn: dominated social media becoming a popular site for professionals and job seekers.
Click here to read the updates on Rabbit R1 release date, features, specifications, and price
Smart technologies
The rise of smartphones and app stores changed our communication and entertainment methods. It led to the emergence of influencing marketing as some mobile games like Angry Birds, Pokemon Go went viral.
E-commerce and online entertainment
Platforms like Amazon, and Netflix disrupted traditional television and cinema industries. Meanwhile, YouTube helped content creators monetize their videos and change the future of online entertainment.
Internet development after 2019
The internet during the pandemic increased our dependence on online tools for remote work, learning, and entertainment. It shifted most of our physical world to the online world like online classes, remote work, etc. It highlights the importance of cybersecurity.
Remote work and learning
People use online tools for work, learning, communication, and entertainment during worldwide lockdown that started in 2019 but continued. Working Decorum used platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet. Educational institutes used e-learning platforms like Goole Classroom etc.
Online Entertainment
People’s focus diverted more toward streaming services and online gaming during and after the lockdown.
Now and Future of the Internet
Global connectivity is expected to rise due to the general adoption of 5G networks and growth in internet speed. It seems like internet things will grow enabling smart homes, cities, industries, and cars by linking more devices.
There will also be more sophisticated security and privacy solutions due to the growing connectivity and use of smart devices. It will enable more advanced cybersecurity with the more advanced invention of the internet in the future.
We will also discover the future of the internet as AI continues to move forward as smart technologies and AI have advanced to unimaginable levels.
Read More:
- Sea creature turns into a baby when it is stressed out showing time travel
- Realme Narzo 70 Turbo 5G launch date, features, specifications & price
- European Space Agency printed 3D metal part in space for first time
- Earth’s mysterious Alaska triangle where over 20,000 people disappeared
- Philips Hue launched a new smart lighting solution for kitchen
- NASA to launch life-searching spacecraft to Jupiter’s moon Europa
Share this content:








Post Comment